What is Java/Android?
Java
The term “core” refers to the fundamental notion of anything, while the phrase “Core Java” refers to the fundamental concept of the Java programming language. We are all aware that Java is one of the most well-known and frequently used programming languages, and that a novice should begin with Core Java and work their way up to Advance Java. Java programming language is a general-purpose programming language based on the object-oriented programming (OOPs) paradigm. Java’s ocean is too deep to learn, i.e., the more you study, the deeper it becomes. Java is a powerful and platform-independent programming language. Java follows the WORA philosophy, which stands for Write Once, Run Anywhere. The programming language is straightforward and simple to grasp. However, it is important to note that Core Java is not the same as Java. Although Java is self-contained, it is normal for newcomers to start with the fundamentals of the language. In reality, there are several editions of Java, with Core Java being one of them.
Android
Android is an open source and Linux-based Operating System for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Android was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google, and other companies.
Android offers a unified approach to application development for mobile devices which means developers need only develop for Android, and their applications should be able to run on different devices powered by Android.
The first beta version of the Android Software Development Kit (SDK) was released by Google in 2007 where as the first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released in September 2008.
On June 27, 2012, at the Google I/O conference, Google announced the next Android version, 4.1 Jelly Bean. Jelly Bean is an incremental update, with the primary aim of improving the user interface, both in terms of functionality and performance.
The source code for Android is available under free and open source software licenses. Google publishes most of the code under the Apache License version 2.0 and the rest, Linux kernel changes, under the GNU General Public License version 2.
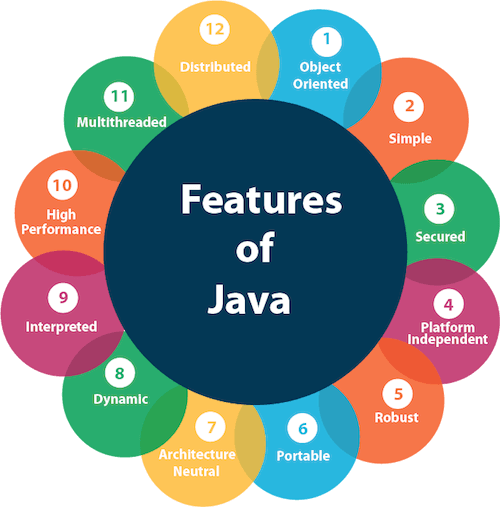
Features



Java Modules
- • Module 1 – Basic of Java
- • Module 2 – Class, Objects, and Types of Classes
- • Module 3 – Packages in Java
- • Module 4 – Data Types in Java
- • Module 5 – Variables, Constraints, and Literals
- • Module 6 – Methods in Java
- • Module 7 – Constructor in Java
- • Module 8 -- Functions & Recursion
- • Module 9 – Arrays & Strings
- • Module 10 – Modifiers in Java
- • Module 11 – Static Keyword, Inheritance, Polymorphism & Encapsulation
- • Module 12 – File Handling & Pointers
- • Module 13 –Final Keyword
- • Module 14 – Inner Class in Java
- • Module 15 – Exception Handling
Android Modules
- • Module 1 – Android Basics
- • Module 2 – Kotlin Basics
- • Module 3 – Intermediate UI
- • Module 4 – Property Finder App UI
- • Module 5 – Advanced UI & Todo App
- • Module 6 – Touches & Animation
- • Module 7 – Memory
- • Module 8 -- Maps & Location
- • Module 9 – Testing & Debugging
- • Module 10 – Media & Devices
- • Module 11 – Multitasking & Persistent Testing, Data
- • Module 12 –Todo List in Room
- • Module 13 –Networking & Web
- • Module 14 –Firebase
- • Module 15 –Cloud Todo List
