What is Embedded System?

Knowledge about Embedded System
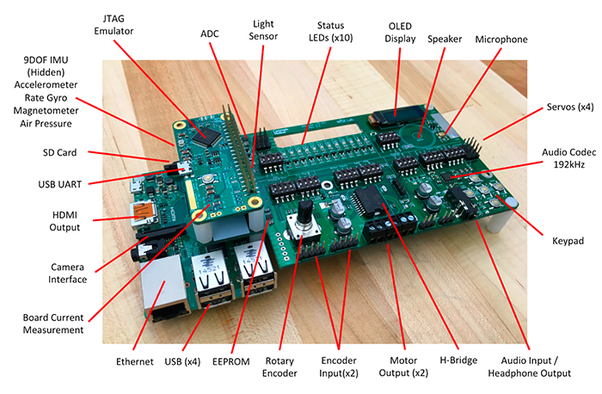
Components of Embedded Systems:
Microcontroller/Microprocessor:The core processing unit responsible for executing instructions and controlling the overall operation of the embedded system.
Memory: Stores program code and data. It includes both read-only memory (ROM) for storing permanent data and random-access memory (RAM) for temporary data storage.
Input/Output (I/O) Interfaces: Connect the embedded system to external devices, sensors, and actuators. These interfaces enable communication with the system’s surroundings.
Sensors and Actuators: Sensors collect data from the environment, while actuators perform actions based on the system’s computations. They are crucial for embedded systems in applications such as robotics and automation.
Communication Interfaces: Enable communication between the embedded system and external devices or networks. This can include interfaces such as UART, SPI, I2C, Ethernet, or wireless communication protocols.
Real-Time Clock (RTC): Keeps track of time and is essential for applications that require time-sensitive operations.
Power Supply: Provides the necessary power for the embedded system to operate. In battery-powered devices, power management is a critical consideration.
Operating System (OS) or Real-Time Operating System (RTOS): Some embedded systems use a lightweight operating system or real-time operating system to manage tasks, scheduling, and resource allocation.


Embedded Modules
- • Module 1 – Hardware Modules
- • Module 2 – Software Modules
- • Module 3 – Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- • Module 4 – Input/Output (I/O) Modules
- • Module 5 – Power Management Modules
- • Module 6 – Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- • Module 7 – Security Modules
- • Module 8 -- Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
- • Module 9 – Microprocessors
- • Module 10 – Microcontrollers
- • Module 11 – Arduino Design
- • Module 12 – Circuit Design
- • Module 13 – Digital System Processing
- • Module 14 – Digital-to-Analog Converters (DAC)
- • Module 15 –Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADC)
